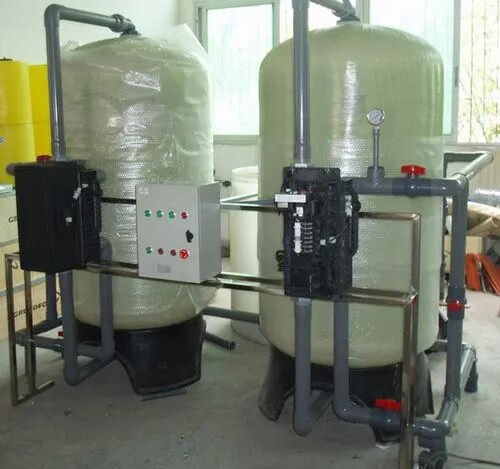
Introduction
The multi-media filter is a water filtration system that uses multiple layers of filter media to
remove particles and impurities from water. Unlike single-media filters that use only one filter
material, multimedia filters combine different materials, each with a specific function, to achieve
more efficient filtration. For example, quartz sand removes suspended matter from water, activated
carbon decolorizes and removes suspended matter from water, manganese sand removes iron and manganese
and suspended matter from water, fiber balls and walnut shells remove oil from water, etc.
The most common multimedia filter consists of sand and anthracite as the filtration media. The sand
has smaller grains and is heavier than the anthracite. This ensures that the sand layer settles
beneath the anthracite and provides finer filtration. A well operated Multimedia Filter can remove
particulates down to 20 microns. This multi-layered approach allows multi-media filters to remove a
wide range of particle sizes, from large sediments to fine particulates, resulting in cleaner and
clearer water.
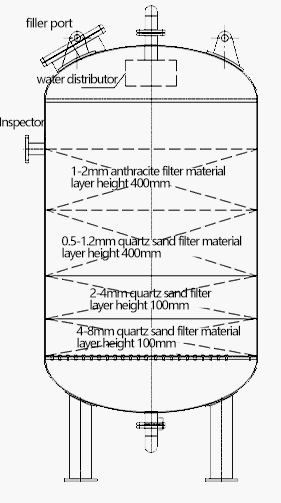

Components
1.Filter Tank: This component will house the filtration media, it is either stainless steel, FRP or
epoxy coated steel. Metallic tanks can handle higher temperatures and pressure
2. Media: This is the filtration media that includes different layers of gravels, quartz sand, and
anthracite. This will depend on the quality of the filtered water that is needed.
3. Internal upper and bottom distributors: The bottom distribution system will prevent the media from
escaping, while the upper distribution system will distribute the flow harmonically during the service
cycle. The materials of construction can either be schedule PVC or stainless steel. If your
application has a high temperature water, we recommend stainless steel internals, tank and face
piping.
4. Valves: The valves open and close according to the different cycles. They could be automatic
electric or pneumatic valves for automatic water filters, or manual valves for manual filters. For
seawater, it is recommended to use nonmetallic valves. Some industries do not allow electric
valves.
5. Controller: This component will control the automation of your filter. This could be a PLC. This is
usually a preference based on the main control in the facility or the building.
6. Face piping: Face piping will connect all valves that control the different cycles. It could be
schedule PVC, stainless steel or epoxy coated carbon steel. The material of the piping depends on the
temperature or operating pressure, and if it’s an indoor or outdoor application.
Application
· Suspended solids and turbidity reduction
· Iron and manganese removal
· Groundwater remediation
· Pre-treatment for RO/NF and membrane system
· Pre-treatment for UV sterilizers
· Filtration of grey, river or surface water
· Tertiary treatment for waste water
· Cooling tower and heat exchanger
· Water features (fountains, etc.)
1. Pretreatment media filter for reverse osmosis (RO):
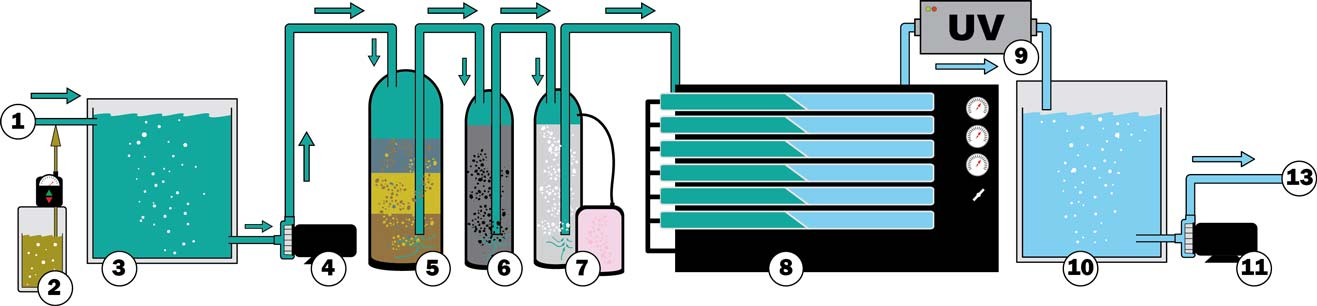
2. Pretreatment media filter for ultraviolet (UV):
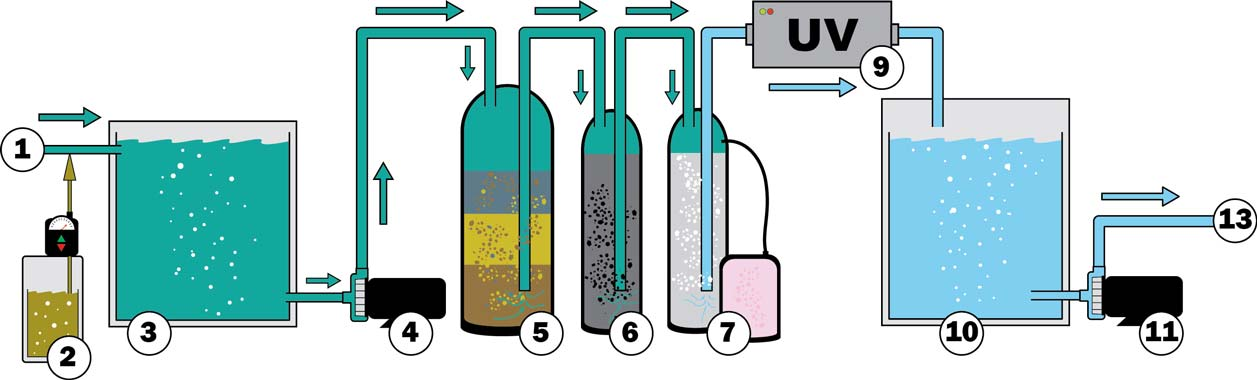
3. Pretreatment media filter for electrodeionization (EDI):
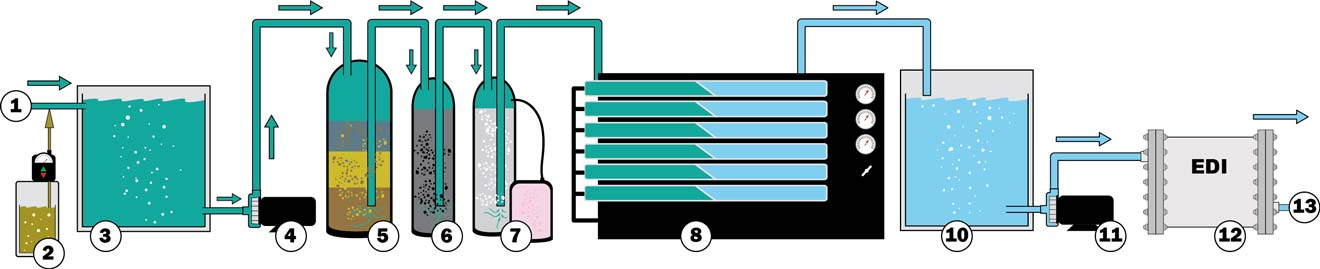
4. Pretreatment media filter for ion exchange:
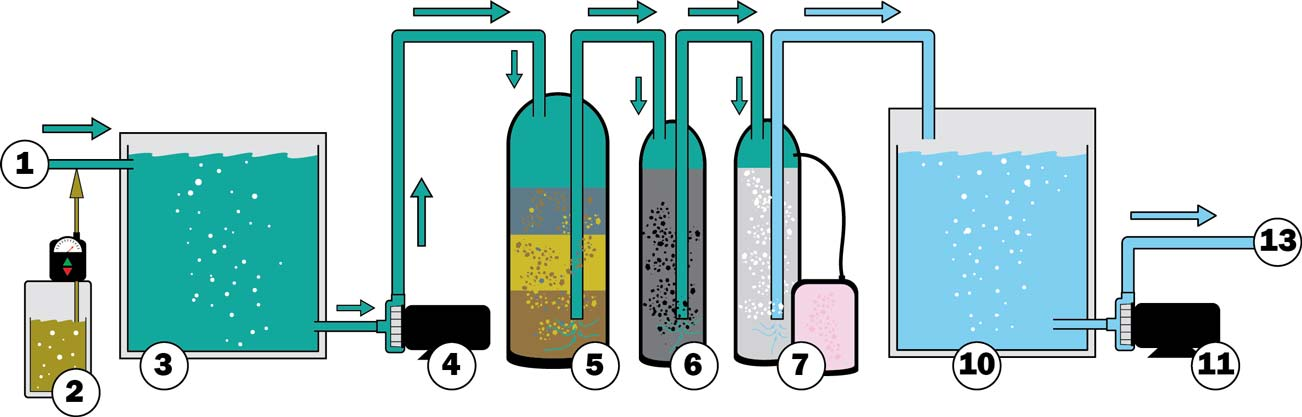
①Raw Feed Water
②Chemical Dosing
③Raw Feed Water Tank
④Feed Pump
⑤Multimedia Filter
⑥Carbon Filter
⑦Ion Exchange Filter
⑧Reverse Osmosis System
⑨Ultra Violet Sterilizer
⑩Product Water Tank
⑪Product Water Pump
⑫Electro-Deionization
⑬Point of Use






