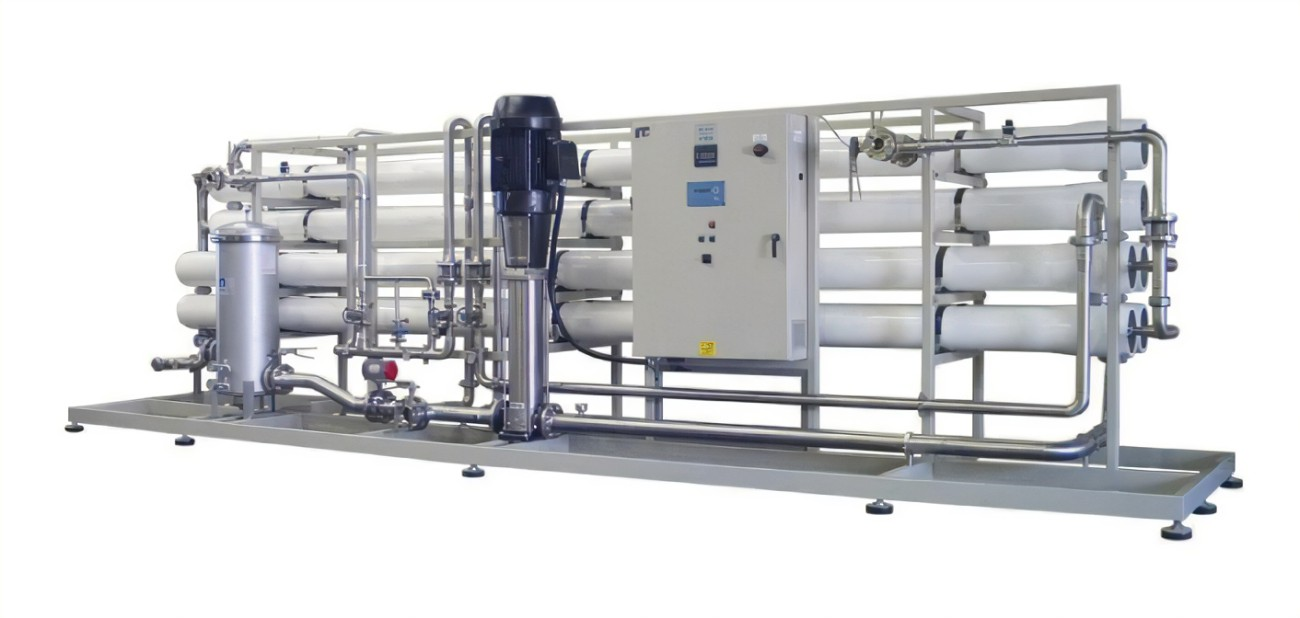
Introduction
Reverse osmosis is a membrane separation technology that uses pressure as the driving force by means
of a selective permeability (semi-permeable) membrane. When the pressure added in the system is
greater than the osmotic pressure of the incoming water solution, water molecules continuously pass
through the membrane, flow into the central tube through the water production channel, and then flow
out at one end. Impurities in the water, such as ions, organic matter, bacteria, viruses, etc., are
trapped on the inlet side of the membrane, and then flows out at the outlet end of the concentrated
water to achieve the purpose of separation and purification.
Features
1. Large water permeability and high salt rejection rate. Under normal circumstances ≥98%
2. It has a high interception and removal effect on organic matter, colloids, particles, bacteria,
viruses, heat sources, etc.
3. Low energy consumption, high water utilization, and lower operating costs than other desalination
equipment.
4. There is no phase change in the separation process and it is reliable and stable.
5. The equipment is small in size, simple to operate, easy to maintain, highly adaptable and has a
long service life.
Working Principle
Application
Food and beverages
Electronics industy
Sea Water Desalination
Medical industry
The chemical industry
Power Generation